Pointer, Array and Introduction to Data Structures
- Array: stores data in consecutive memory locations and are referenced by index. It is more efficient then storing manually. Index always starts from 0.
In example:
Program manually stored without array:
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int number1;
int number2;
int number3;
int number4;
int number5;
number1 = 10;
number2 = 20;
number3 = 30;
number4 = 40;
number5 = 50;
printf( "number1: %d\n", number1);
printf( "number2: %d\n", number2);
printf( "number3: %d\n", number3);
printf( "number4: %d\n", number4);
printf( "number5: %d\n", number5);
}
Program using array:
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int number[10]; /* number is an array of 10 integers */
int i = 0;
/* Initialize elements of array n to 0 */
while( i < 10 )
{
/* Set element at location i to i + 100 */
number[ i ] = i + 100;
i = i + 1;
}
/* Output each array element's value */
i = 0;
while( i < 10 )
{
printf("number[%d] = %d\n", i, number[i] );
i = i + 1;
}
return 0;
}
There are some operation that can be performed in arrays :
- Traversal
- Insertion
- Sorting
- Searching
- Deletion
- Merging
Pointer: is a programming language object, whose value refers to (or “points to”) another value stored elsewhere in the computer memory using its address
2 symbols in pointer:
&: Address Operator
*: Deferencing Operator
Using Pointer:
in example a declaration:
- int x;
- int*p = &x;
So there is an integer x, and a pointer p. P took a value from an integer that is pointed. In this case P is pointed to x’s address. In conclusion, the value of x will be also the value of pointer P.
If we declare that x=10; or we can write *p = 10;
then *p and x has a value of 10.
Data Structure:
- A data structure is an arrangement of data, either in the computer’s memory or on the disk storage
- is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently
Here are some examples of data structures:
- Arrays
- Linked Lists
- Queues
- Stacks
- Binary Trees
- Hash Tables
Linked Lists:
The pointer always points to the next member of the list. If the pointer is NULL, then it is the last node in the list.
A linked list is held using a local pointer variable which points to the first item of the list. If that pointer is also NULL, then the list is considered to be empty.
Queue:
- is a particular kind of abstract data type or collection in which the entities in the collection are kept in order and the principal (or only) operations on the collection are the addition of entities to the rear terminal position
- The elements in a queue are added at one end called the rear and removed from the other end called the front
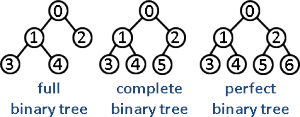
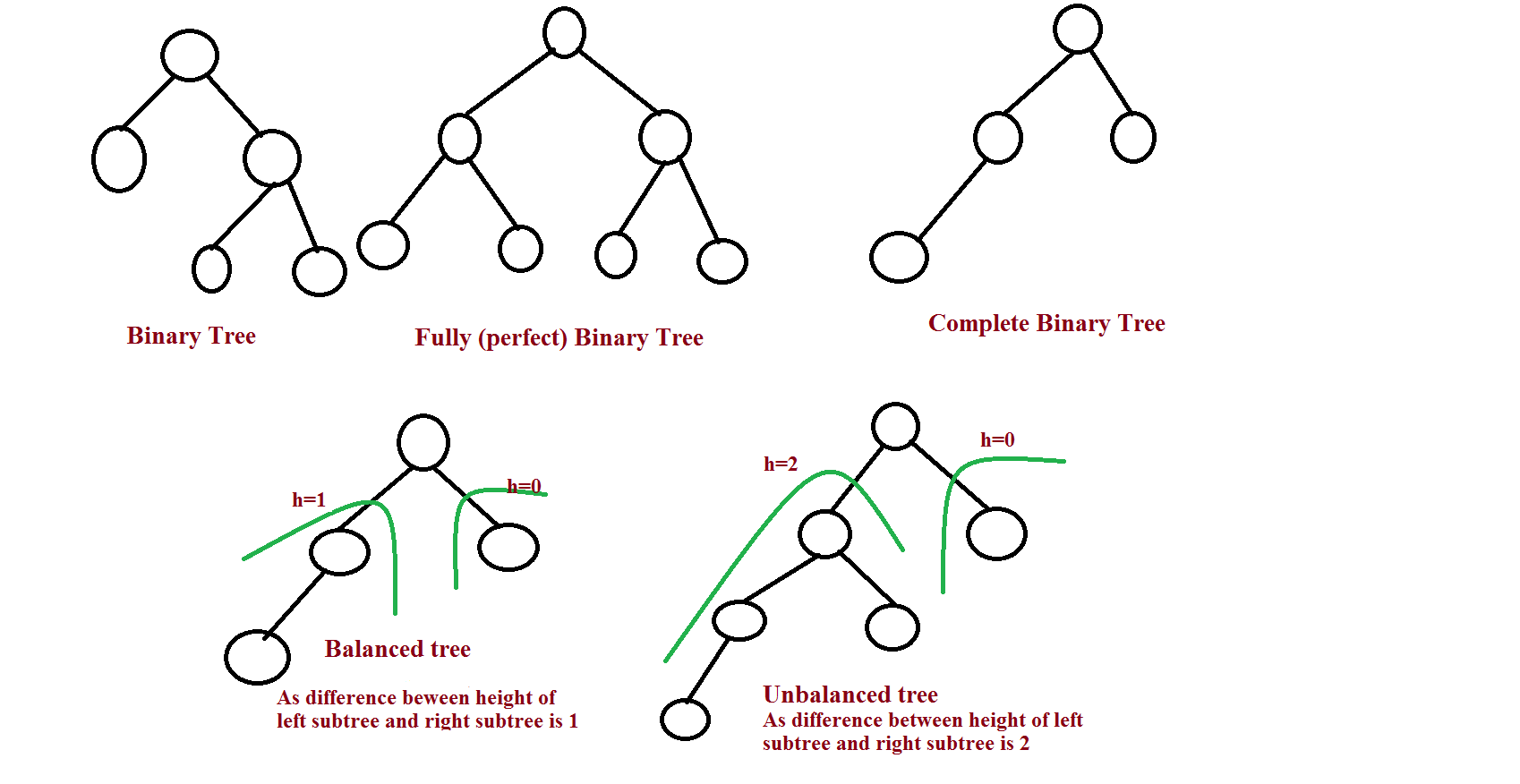
Binary Trees:
- is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child.
- data structure which is defined as a collection of elements called the nodes
- Every node contains a left pointer, a right pointer, and a data element
Abstract Data Types:
- is a mathematical model for data types where a data type is defined by its behavior (semantics) from the point of view of a user of the data, specifically in terms of possible values, possible operations on data of this type, and the behavior of these operations.
- C/C++ has a concept called class and struct which assist the programmer in implementing abstract data type.
- For example, integers are an ADT, defined as the values …, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, …, and by the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, together with greater than, less than, etc., which behave according to familiar mathematics (with care for integer division), independently of how the integers are represented by the computer.
Talking about Structure:
- Structure
- Nested Structure
- and Array of Struct
Example of a Structure:
struct x{
int x;
char b;
};
x data;
x is a data type like integer and float, and data is the variable.
Example of a Nested Structure:
There is a struct inside a struct.
struct profile {
int age;
char name[100];
};
struct student {
struct profile p;
int score;
char grade;
};
student x;
x.score = 92;
x.grade = ‘A’;
x.p.age = 20;
strcpy(x.p.name,”budi”);
Example of Array of Structure:
struct profile {
int age;
char name[100];
};
struct student {
struct profile p;
int score;
char grade;
};
student arr[10];
arr[0].score = 92;
arr[0].grade = ‘A’;
arr[0].p.age = 20;
strcpy(arr[0].p.name,”budi”);
arr[1].score = 83;
arr[1].grade = ‘b’;
arr[1].p.age = 19;
strcpy(arr[1].p.name,”chandra”);
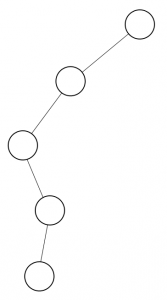 <skewed Binary tree
<skewed Binary tree