Tree and Binary Tree
- Type of Binary Tree
- Property of Binary Tree
- Representation of Binary Tree
- Threaded Binary Tree Concept
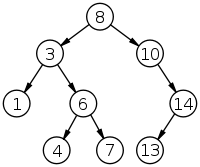
A sample of binary tree with 9 nodes, depth of 3, with 8 on the root. Leaves are nodes which contain 4, 7, 13.
Type of Binary Tree
- Perfect binary tree : is a binary tree that every level are at the same depth
- Complete binary tree : every level except the last level is completely filled, a perfect binary tree must be complete.
- Skewed binary tree : is a binary tree that every depth/each node has only 1 child at most.
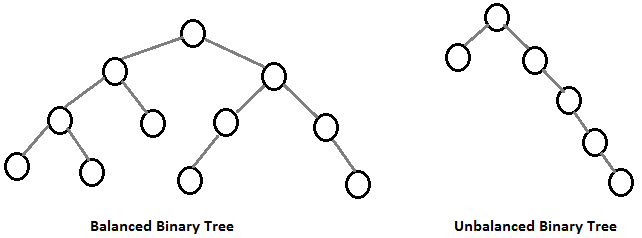
- Balanced binary tree : is a binary tree which no leaf is farther away from the root than any other leaf
Maximum number of nodes on level k of a binary tree is 2^k.
Maximum number of nodes on a binary tree of height h is 2^(h+1) – 1.
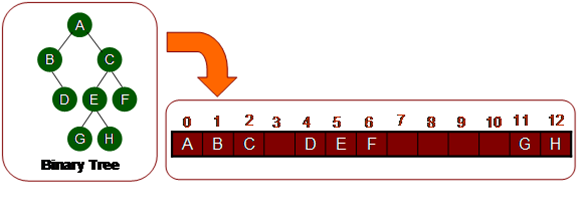
Implementation of binary tree using array:
Index on array represents node number
Index 0 is Root node
Index left child is 2p+1, p = parent index
index right child = 2p + 2
index parent is (p-1)/2
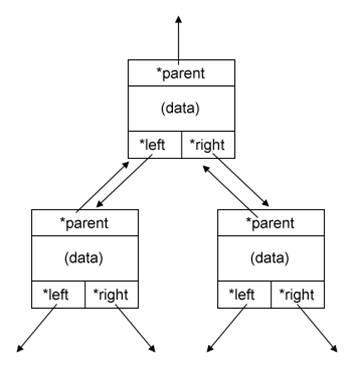
Implementation using linked list:
struct tree{
int number;
struct tree *left, *right, *parent;
};
struct tree *root = NULL;
Threaded Binary Tree
- is same as binary tree but with a difference in storing NULL pointers.