Data Structures 02
Guest: Pak Bong Defendy, Binusian 2007
Topics:
- Big Data (Structured & Unstructured)
- Cloud Platform
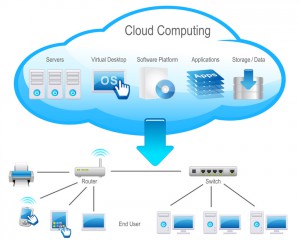
Cloud Platform:
- Cloud uses 2 centers to store datas: Data Center and Data Recovery Center.
- Data Center is used to store new datas from customers/users.
- Data Recovery Center is used to prevent in missing or corrupted datas.
- Cloud Platform is a platform for cloud computing.
Cloud Computing
- is a kind of Internet-based computing that provides shared processing resources and data to computers and other devices on demand.
- Every data we have can be stored in cloud storages that will be stored in a Data Center.
- Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform are the examples of Cloud. The nearest Microsoft’s data center is at Singapore.
- Cloud computing has become a highly demanded service or utility due to the advantages of high computing power, cheap cost of services, high performance, scalability, accessibility as well as availability.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- DOWNTIME :
This may be one of the worst disadvantages of cloud computing. No cloud provider, even the very best, would claim immunity to service outages. Cloud computing systems are internet based, which means your access is fully dependent on your Internet connection.
- SECURITY AND PRIVACY :
Any discussion involving data must address security and privacy, especially when it comes to managing sensitive data. We mustn’t forget code space and what happened to it after its AWS EC2 console was hacked and its data eventually deleted, forcing the company to close doors forever. Of course, your cloud service provider is expected to manage and safeguard the underlying hardware infrastructure of a deployment, however remote access is your responsibility and, in any case, no system is perfectly secure. You’ll have to carefully weigh all the risk scenarios.
- Etc
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Flexible
- Disaster Recovery
- Work from ANYWHERE
- Etc
BIG DATA
- Big datais a term for data sets that are so large or complex that traditional data processing applications are inadequate. Challenges include analysis, capture, data curation, search, sharing, storage, transfer, visualization, querying and information privacy.
- Big Data are growing rapidly in part because they are increasingly gathered by cheap and numerous information-sensingmobile devices, aerial (remote sensing), software logs, cameras, microphones, radio-frequency identification (RFID) readers and wireless sensor networks.
- Big Data has structured and unstructured data, every data connects to each other.
- Big data usually includes data sets with sizes beyond the ability of commonly used software tools to capture, curate, manage, and process data within a tolerable elapsed time.